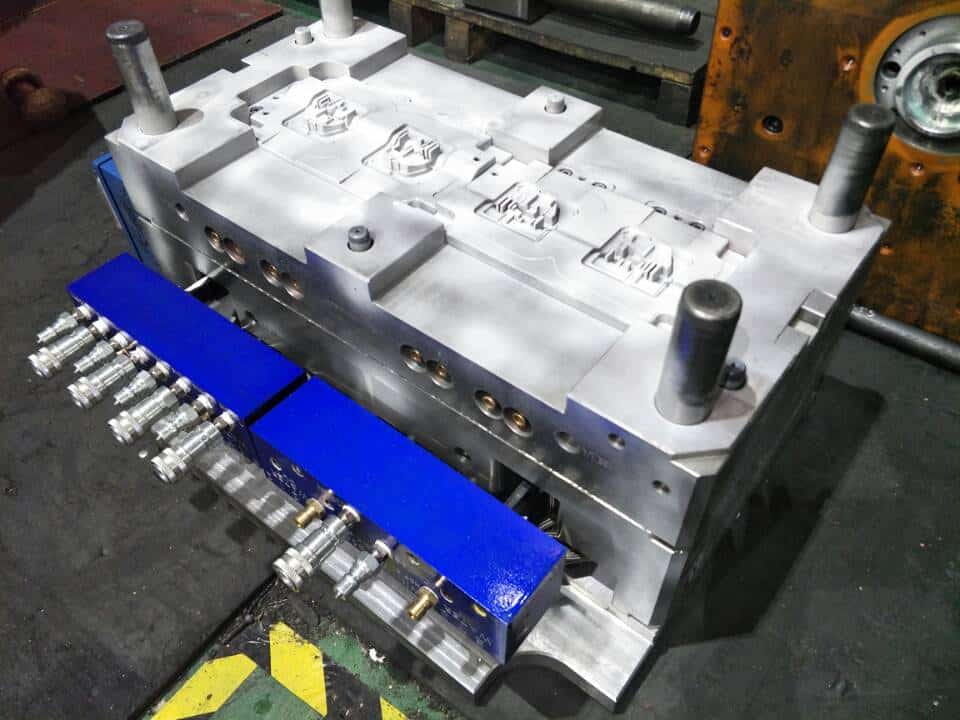
Commonly used thermosetting plastic moulds and their molding characteristics
Thermosetting plastic mold has a large stiffness, elastic and plastic deformation under load, and the temperature has little effect on the stiffness, under the same load and temperature conditions, creep is much smaller than the thermoplastic mold; good heat resistance, the plastic parts are quite stable to heat after curing; good dimensional stability of plastic parts. Affected by temperature and humidity and molding shrinkage is small, plastic size accuracy than thermoplastic mold to high; excellent electrical properties; good corrosion resistance, not subject to strong acids, weak alkalis and organic solvents corrosion; plastic mold processability is good, you can use a variety of molding methods processing and other advantages. The disadvantage is that the mechanical properties are poor.
plastic injection mold
Commonly used thermosetting plastic moulds and their molding properties:
(1) phenolic plastic mold
① good formability, suitable for compression molding, partly for extrusion molding, individual for injection molding;
②Contains moisture, volatile matter, should be preheated, exhaust. Those who do not preheat should increase the mold temperature and molding pressure and pay attention to the exhaust;
③shrinkage and directionality is generally larger than the amino plastic mold;
④Mold temperature has a great influence on the fluidity, generally more than 160 ℃ when the fluidity drops rapidly;
⑤Hardening speed is generally slower than that of amino, and the heat released during hardening is large, and the internal temperature of thick-walled large plastic parts is easy to be too high, so it is easy to occur uneven hardening and overheating.
(2)Amino plastic mold
①Molding shrinkage rate is large, urea formaldehyde plastic mold is not suitable for pressure injection of large plastic parts;
② good fluidity, hardening speed, so preheating and molding temperature to be appropriate, loading, mold and pressurization speed to be fast;
③More water volatiles, easy to absorb moisture, caking, molding should be preheated and dry, and to prevent moisture absorption, but too dry, the liquidity decreases. There are moisture and decomposition material when molding, there is weak acidity, the mold should be chrome plated to prevent corrosion, and exhaust when molding;
④Molding temperature has a greater impact on the quality of plastic parts. High temperature is easy to decomposition, discoloration, bubbles, cracking, deformation, uneven color; low temperature, poor liquidity, not glossy, so the molding temperature should be strictly controlled;
⑤ Fine material, large mass volume, more inflatable material, easy to occur ripples and flow marks when forming large plastic parts with pre-pressed ingots, so generally not suitable;
⑥Brittle, easy stress concentration around the insert, poor dimensional stability;
(7) When the storage period is long and the storage temperature is high, it will lead to a rapid decline in fluidity.
(3)Silicone plastic mold
①Good fluidity, slow hardening speed, used in compression molding;
②To be pressed at higher temperature;
③To be cured by high temperature after compression molding Molding characteristics.
(4) Polysiloxane
①Mainly used for low-pressure extrusion molding, encapsulation of electronic components, etc. The general molding pressure is 4 to 10MPa, molding temperature is 160 to 180℃;
②Excellent fluidity, easy to overflow, small shrinkage, high storage temperature, fluidity will decline rapidly;
③Hardening speed is slow, the molding needs high temperature curing, easy to occur after shrinkage, plastic thickness greater than 10mm should gradually increase the temperature and extend the appropriate holding time, otherwise easy to brittle crack;
④When used for encapsulating electronic components such as integrated circuits, the location and cross-section of the inlet should be careful to prevent the molten material from flowing too fast or directly impacting the weak components, and it is appropriate to open an overflow groove in the opposite direction of the inlet, which is generally used in one mold with multiple cavities, and the cross-section of the main channel should not be too small.
(5)Epoxy resin
①Good fluidity, fast hardening speed;
②Small shrinkage of hardening, but thermal rigidity is not easy to get off the mold; generally no exhaust when hardening, and should be pressurized immediately after loading;
③Preheating temperature is generally 80 to 100℃, molding temperature is 140 to 170℃, molding pressure is generally 10 to 20MPa, and holding time is generally 0.6min/mm;
④Often applied to casting molding and low-pressure extrusion molding, for encapsulating electronic components, etc.
(6)Glass fiber reinforced plastic mold
①The fluidity is worse than general plastic mold, but the material penetration force is strong, the flying edge is thick and not easy to remove. Therefore, when choosing the parting surface, attention should be paid to the direction of the flying edge. The upper and lower molds and inserts should be taken as a whole structure, if the combination structure is used, the assembly gap should not be taken large, the upper and lower molds can be removed molding parts should be taken 1T8 to 1T9 level clearance fit;
② shrinkage is small, the shrinkage rate is generally taken 0.1% to 0.2%, but there is directional, prone to poor fusion, deformation, warping, shrinkage, cracks, stress concentration and resin filler distribution and other phenomena. Thin-walled parts are fragile, not easy to demold, and large plastic parts are prone to corrugation and material accumulation;
③Molding pressure, material infiltration and extrusion force, mold core and plastic insert should have sufficient strength to prevent deformation, displacement and damage, especially the slender core and the cavity gap between the small should be more attention;
④ quality volume, compression ratio are larger than the general plastic mold. Therefore, the design of the mold should take a larger filling room, the general volume of the material to take 2-3 times the volume of plastic parts;
⑤ suitable for molding through-hole, avoid molding such as the diameter of 5mm below the blind hole. Large plastic parts as far as possible not to design small holes. Hole spacing and hole edge distance should be taken as a large value, large density arrangement of small holes should not be pressure plastic molding. When forming blind holes, the bottom should become a hemispherical or conical surface, in order to facilitate the flow of materials. The ratio of hole diameter to hole depth is generally 1:2 to 1:3;
⑥The direction of pressurization should be chosen from the direction of the large projection surface of the plastic part, not the part with high dimensional accuracy and the vertical direction of the axis of the insert and core;
(7) The slope of mold release should be more than 1°. The top bar should have sufficient strength and even distribution of ejecting force, and the top bar should not be used as a core;
⑧ Fast molding material can be demolded at molding temperature, slow molding material mold should be heated and strong cooling measures.






