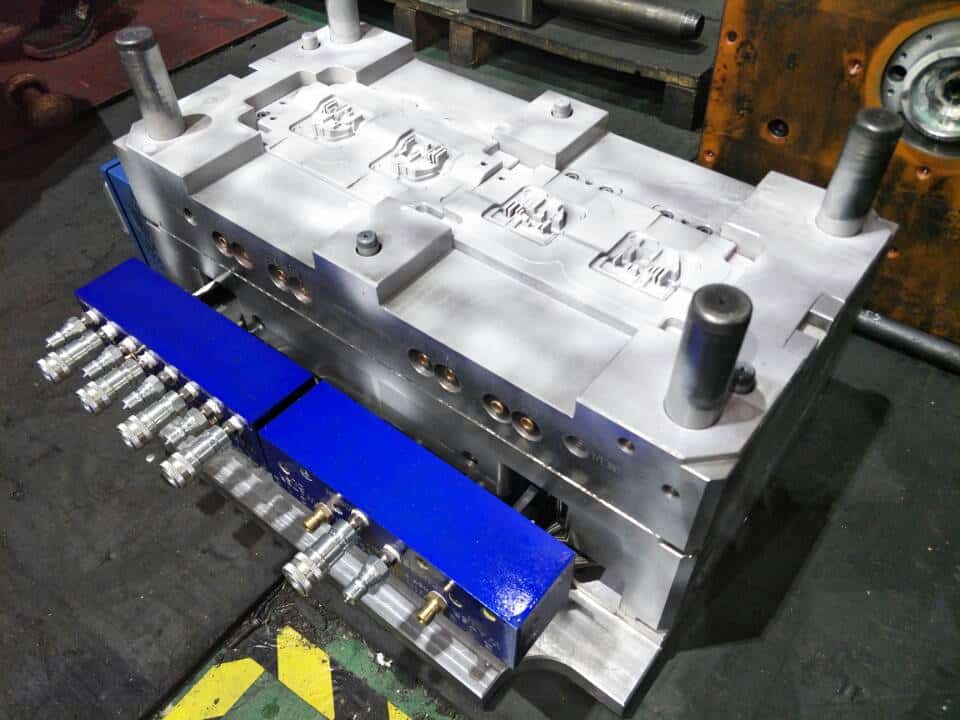
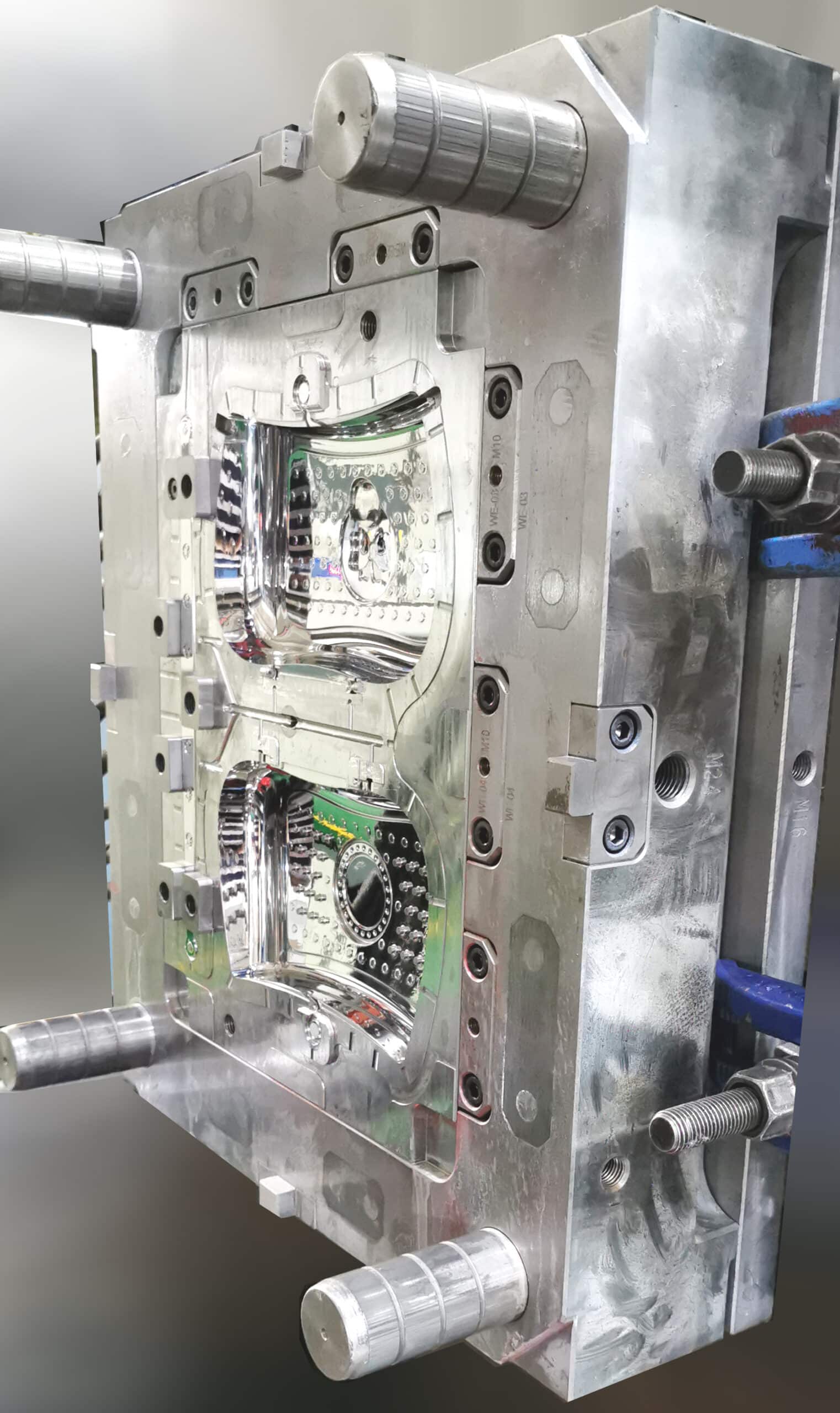
Several Practical Tips For Mold Tooling To Reduce Defects!
In order to improve the use performance of the mold, many manufacturers will properly process their molds. Mold processing refers to the processing of the forming and blank making tools, and also includes the shear mold and die cutting mold. However, in many cases, the mold processing will also reflect the processing defects, leading to the decline of the mold performance. How to build mold processing defects? The following seven measures can build mold processing defects.
1. Reasonable selection and dressing of grinding wheel
The grinding wheel made of white corundum is better. Its performance is hard and brittle, and it is easy to produce new cutting edges. Therefore, the cutting force is small and the grinding heat is small. In terms of grain size, medium grain size is better, such as 46~60 mesh. In terms of hardness, medium soft and soft (ZR1, ZR2 and R1, R2) are used, that is, coarse grain and low hardness grinding wheels. Good self excitation can reduce the cutting heat. It is very important to select appropriate grinding wheel during fine grinding. GD single crystal corundum grinding wheel is more suitable for the high vanadium and high molybdenum condition of die steel. When machining hard alloy and quenching materials with high hardness, diamond grinding wheel with organic binder is preferred. The grinding wheel with organic binder has good self grinding performance, and the roughness of the ground workpiece can reach Ra0.2 μ m. In recent years, with the application of new materials, CBN (cubic boron nitride) grinding wheel has shown a very good machining effect, which is superior to other types of grinding wheels in precision machining on CNC forming grinder, coordinate grinder, CNC internal and external grinder. During grinding, the grinding wheel shall be trimmed in time to keep its sharpness. When the grinding wheel is passivated, it will rub and squeeze on the workpiece surface, causing burns on the workpiece surface and reducing the strength.
2. Rational use of cooling and lubricating fluid
Give play to the three functions of cooling, washing and lubrication to keep cooling, lubrication and cleaning, so as to control the grinding heat within the allowable range to prevent thermal deformation of the workpiece. Improve the cooling conditions during grinding, such as using oil immersed grinding wheel or internally cooled grinding wheel. When the cutting fluid is introduced into the center of the grinding wheel, the cutting fluid can directly enter the grinding area to play an effective cooling role and prevent the workpiece surface from burning.
3. Minimize quenching stress after heat treatment
Because the quenching stress and the network carbide structure under the effect of grinding force, the phase transformation of the structure is very easy to cause cracks in the workpiece. In order to eliminate the residual stress of grinding for high-precision dies, low temperature aging treatment should be carried out after grinding to improve the toughness.
The vacuum heat treatment of mould includes preliminary heat treatment, final heat treatment and surface strengthening treatment. Generally, heat treatment defects refer to various defects that occur in the final heat treatment process or in subsequent processes and during the use of the mold, such as quenching cracks, deformation out of tolerance, insufficient hardness, electro machining cracks, grinding cracks, early damage of the mold, etc. Now let’s follow the small editor to learn more about these defect prevention measures! picture
Hot Runner Molds
Quenching crack
The causes of quenching cracks and preventive measures are as follows:
1. The shape effect is mainly caused by design factors, such as too small fillet R, improper hole location, and poor section transition.
2. Overheating (overburning) is mainly caused by inaccurate temperature control or temperature loss, nonstandard and unreasonable vacuum heat treatment process, especially inadequate tempering. The setting temperature is too high and the furnace temperature is uneven. The preventive measures include maintenance, checking the temperature control system, correcting the process temperature, and adding sizing iron between the workpiece and the furnace floor.
3. Decarburization is mainly caused by overheating (or overburning), unprotected heating of air furnace, small machining allowance, residual decarburization layer in forging or preparatory heat treatment and other factors. The preventive measures are controlled atmosphere heating, salt bath heating, and the vacuum furnace and box furnace are protected by packing or use of anti oxidation coating; The machining allowance is increased by 2-3 mm.
4. Improper cooling is mainly caused by improper selection of coolant or undercooling. The cooling characteristics of quenching medium or tempering treatment should be mastered.
5. The raw materials have poor structure, such as severe carbide segregation, poor forging quality, improper preparation heat treatment method, etc. The preventive measures are to adopt correct forging process and reasonable preparation heat treatment system.
Insufficient hardness
The causes and preventive measures of insufficient hardness are as follows:
1. The quenching temperature is too low, which is mainly caused by improper process setting temperature, temperature control system error, improper method of loading or entering the cooling tank, etc. The process temperature should be corrected, the temperature control system should be checked, and the workpiece should be placed evenly at reasonable intervals during loading. The workpiece should be scattered into the tank and should not be stacked or bundled into the tank for cooling.
2. The quenching temperature is too high, which is caused by improper process setting temperature or temperature control system error. The process temperature should be corrected, and the temperature control system should be checked and repaired.
3. Overtempering, which is caused by too high tempering temperature setting, fault error of temperature control system or furnace entry when the furnace temperature is too high, shall correct the process temperature, check and repair the temperature control system, and shall not be loaded higher than the set furnace temperature.
4. The reason for improper cooling is that the pre cooling time is too long, the cooling medium is not properly selected, the temperature of the quenching medium is gradually higher and the cooling performance is reduced, the mixing is poor or the temperature of the tank is too high. Measures: the furnace and the tank shall be discharged quickly; Master the cooling characteristics of quenching medium; The oil temperature is 60~80 ℃, and the water temperature is below 30 ℃. When the cooling medium is heated due to large quenching amount, the cooling quenching medium shall be added or other cooling tanks shall be used for cooling; Strengthen the mixing of coolant; Take it out at Ms+50 ℃.
5. Decarburization, which is caused by residual decarburization layer of raw materials or quenching heating. The preventive measures are controlled atmosphere heating, salt bath heating, vacuum furnace and box furnace are protected by encasing or anti oxidation coating; The machining allowance is increased by 2-3 mm.
Deformation out of tolerance
In mechanical manufacturing, quenching deformation of heat treatment is absolute, while non deformation is relative. In other words, it is just a matter of deformation size. This is mainly due to the surface relief effect of martensitic transformation during heat treatment. It is very difficult to prevent heat treatment deformation (size change and shape change), and in many cases, it has to rely on experience to solve. This is because not only the steel type and die shape have an impact on the heat treatment deformation, but also the improper carbide distribution state and forging and heat treatment methods can cause or intensify it. In many conditions of heat treatment, as long as a certain condition changes, the deformation degree of steel parts will change greatly. Although the problem of heat treatment deformation has been solved mainly by experience and trial method for a long time, it is a very meaningful work to correctly grasp the relationship between raw material forging, module orientation, mold shape, heat treatment method and heat treatment deformation, grasp the heat treatment deformation rules from the accumulated actual data, and establish archives of heat treatment deformation.
decarbonization
Decarburization is the phenomenon and reaction that all or part of the carbon in the surface layer is lost due to the surrounding atmosphere during heating or insulation of steel parts. Decarburization of steel parts will not only cause insufficient hardness, quenching cracks, heat treatment deformation and chemical heat treatment defects, but also have a great impact on fatigue strength, wear resistance and die performance.
Cracks caused by EDM
In mold manufacturing, EDM (electric pulse and wire cutting) is a more and more popular processing method. However, with the wide application of EDM, the defects caused by it also increase correspondingly. As EDM is a processing method to melt the mold surface by virtue of the high temperature generated by the discharge, a white EDM metamorphic layer is formed on the machined surface, and a tensile stress of about 800MPa is generated. In this way, defects such as deformation or cracks often appear in the EDM process of the mold. Therefore, the influence of EDM on die materials must be fully understood and corresponding preventive measures must be taken in advance for the die adopting EDM. Prevent overheating and decarburization during heat treatment, and conduct full tempering to reduce or eliminate residual stress; In order to fully eliminate the internal stress generated during quenching, high temperature tempering is required. Therefore, steel grades that can withstand high temperature tempering (such as Crl2, ASP-23, high-speed steel, etc.) should be used to process under stable discharge conditions; After EDM, it shall be stabilized and relaxed; Set reasonable process holes and grooves; Fully eliminate the re solidified layer for use in a sound state; Based on the principle of vector translation, the concentrated internal stress in the cutting outpost was cut through, drained and released.
Insufficient toughness
The reason for the insufficient toughness may be that the quenching temperature is too high and the holding time is too long, which causes the grain coarsening, or the tempering is not avoided in the tempering brittle zone.
Grinding crack
When there is a large amount of retained austenite in the workpiece, tempering transformation will occur under the action of grinding heat, resulting in structural stress and workpiece cracking. The preventive measures are as follows: after quenching, conduct deep cooling treatment or repeat tempering for many times (generally 2-3 times for mold tempering, even for low alloy tool steel for cold working) to minimize the amount of retained austenite.







