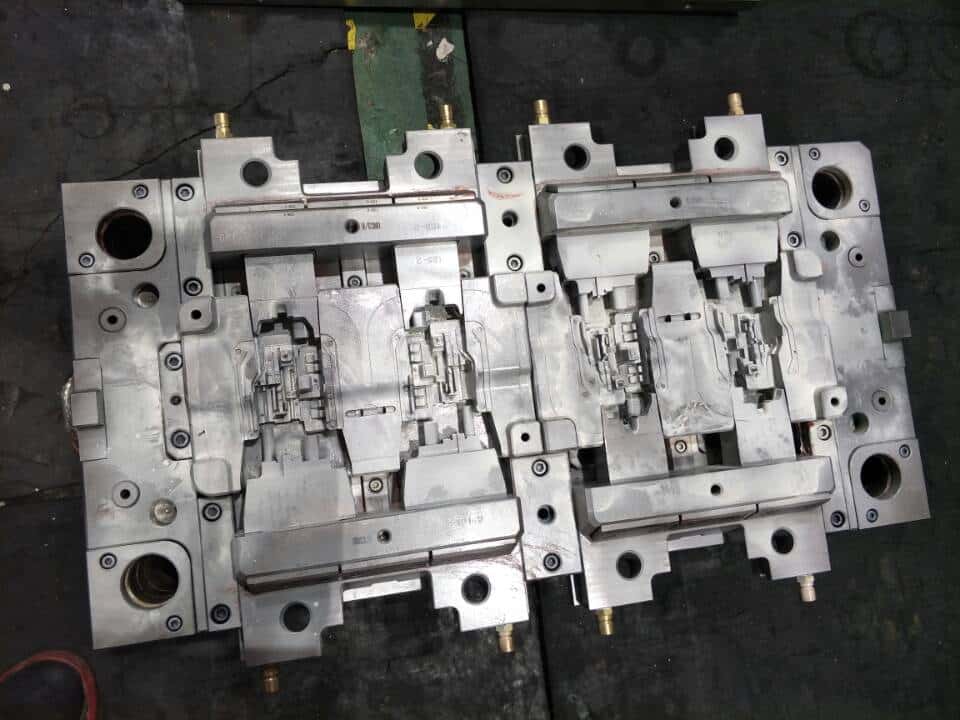
Principle and main structure of injection mold
Injection mold is a part that gives shape and size to plastics during molding. Although the structure of the mold may vary greatly due to different types and properties of plastics, shapes and structures of plastic products, and types of injection machines, the basic structure is the same.
The mold is mainly composed of gating system, molding parts and structural parts. Among them, the gating system and molding parts are the parts that directly contact with the plastic and change with the plastic and products. They are the most complex parts in the plastic mold with the greatest change, and require the highest processing finish and precision.
The gating system refers to the runner part before the plastic enters the mold cavity from the nozzle, including the main runner, cold material cavity, splitter channel and gate. Formed parts refer to various parts that form the shape of products, including moving mold, fixed mold, cavity, core, molding rod, exhaust port, etc. The typical plastic mold structure is shown in the figure.
Mainstream
It is a section of channel in the mold connecting the injection machine nozzle to the shunt channel or cavity. The top of the main runner is concave to connect with the nozzle. The inlet diameter of the main channel shall be slightly larger than the nozzle diameter (O.8mm) to avoid overflow and prevent blocking due to improper connection between the two. The inlet diameter depends on the size of the product, generally 4-8mm. The diameter of the main runner shall be expanded inwards at an angle of 3 ° to 5 ° to facilitate the demoulding of the runner excrescence.
Cold charge cavity
It is a hole at the end of the main runner to catch the cold material generated between two injections at the nozzle end, so as to prevent the blockage of the splitter or gate. Once the cold material is mixed into the mold cavity, internal stress will easily occur in the products. The diameter of the cold charge cavity is about 8-10mm, and the depth is 6mm. In order to facilitate demoulding, the bottom is usually borne by the demoulding rod. The top of the demoulding rod should be designed as a zigzag hook or set with a sink groove, so that the sprue can be pulled out smoothly during demoulding.
Diverging channel
It is the channel connecting the sprue and each cavity in the multi slot die. In order to make the melt fill all cavities at the same speed, the distribution of the shunting channels on the mold should be symmetrical and equidistant. The shape and size of the splitter channel section have influence on the flow of plastic melt, the difficulty of product demoulding and mold manufacturing.
If the flow rate is equal, the resistance of the runner with circular section is the minimum. However, because the specific surface of the cylindrical runner is small, it is unfavorable to the cooling of the shunting channel, and this kind of shunting channel must be set on the two halves of the mold, which is laborious and easy to align.
Therefore, the trapezoidal or semicircular section shunting channel is often used, and it is set on the half mold with the demoulding rod. The runner surface must be polished to reduce flow resistance and provide faster filling speed. The size of the runner depends on the type of plastic, the size and thickness of the product. For most thermoplastics, the section width of the splitter channel is not more than 8m, the extra large one can reach 10-12m, and the extra small one can reach 2-3m. On the premise of meeting the needs, the sectional area shall be reduced as much as possible to avoid increasing the shunting channel burden and prolonging the cooling time.
Gate
It is the channel connecting the main runner (or splitter) and the cavity. The cross-sectional area of the channel can be equal to that of the main channel (or splitter channel), but it is usually reduced. Therefore, it is the part with the smallest sectional area in the whole runner system. The shape and size of gate have a great influence on the quality of products.
The function of the gate is: A. control the material flow speed: B. prevent backflow due to the early solidification of the molten materials in this part during injection; C. increase the temperature of the molten materials passing through by strong shear, thus reducing the apparent viscosity to improve the fluidity; D. facilitate the separation of products from the runner system. The design of gate shape, size and location depends on the nature of plastic, the size and structure of products.
Generally, the section shape of the gate is rectangular or round, and the section area should be small and the length should be short. This is not only based on the above functions, but also because it is easier for a small gate to become larger, while it is difficult for a large gate to shrink. The gate position shall be generally selected at the place where the product is thickest and does not affect the appearance. The design of gate size shall take into account the properties of plastic melt.
Cavity
It is the space for molding plastic products in the mold. The components used to form the cavity are collectively referred to as molded parts. Each molded part often has a special name. The shaped parts forming the product shape are called female die (also called female die), and those forming the internal shape of the product (such as holes, grooves, etc.) are called core or punch (also called male die).
When designing molded parts, the overall structure of the cavity should be determined according to the properties of plastic, the geometric shape of the product, the dimensional tolerance and the use requirements. Secondly, according to the determined structure, the location of parting surface, gate and vent and the demoulding method are selected. Finally, according to the size of the control products, the design of each part and the combination mode of each part are determined. The plastic melt has very high pressure when entering the cavity, so the molding parts should be reasonably selected and checked for strength and stiffness.
To ensure the smooth and beautiful surface of plastic products and easy demoulding, the surface in contact with plastics shall have a roughness of Ra>0.32um and be corrosion resistant. Formed parts are generally made of corrosion-resistant steel by heat treatment to improve the hardness.
Exhaust port
The utility model is a grooved air outlet opened in the mold, which is used for discharging the original gas and the gas brought in by the molten material. When molten material is injected into the mold cavity, the air originally stored in the mold cavity and the gas brought in by the melt must be discharged out of the mold through the exhaust port at the end of the material flow, otherwise the products will have air holes, poor fusion, insufficient mold filling, and even the accumulated air will burn the products due to the high temperature caused by compression.
In general, the air vent can be set at the end of the molten material flow in the mold cavity or on the parting surface of the plastic mold. The latter is a shallow groove with a depth of 0.03-0.2mm and a width of 1.5-6mm at one side of the die. During injection, there will not be a lot of molten materials oozing from the vent hole, because the molten materials will be cooled and solidified there, blocking the channel. The opening position of the exhaust port shall not face the operator to prevent accidental ejection of molten materials from injuring people.
In addition, the fit clearance between the ejector rod and the ejector hole, the fit clearance between the ejector block and the stripper plate and the core can also be used to exhaust.
Structural parts
It refers to various parts constituting the die structure, including various parts for guiding, demoulding, core pulling and parting. Such as front and rear splints, front and rear buckle formworks, pressure bearing plates, pressure bearing columns, guide columns, stripping formworks, stripping rods and return rods.
Heating or cooling device
This is a device to solidify the molten material in the mold. For thermoplastics, it is generally the channel of cooling medium in the male and female mold, and the cooling purpose is achieved by circulating the cooling medium. The cooling medium introduced varies with the type of plastic and product structure, including cold water, hot water, hot oil and steam. The key is efficient uniform cooling. Uneven cooling will directly affect the quality and size of products. The layout of cooling channels and the selection of cooling medium shall be considered according to the thermal properties (including crystallization) of molten materials, the shape of products and mold structure.
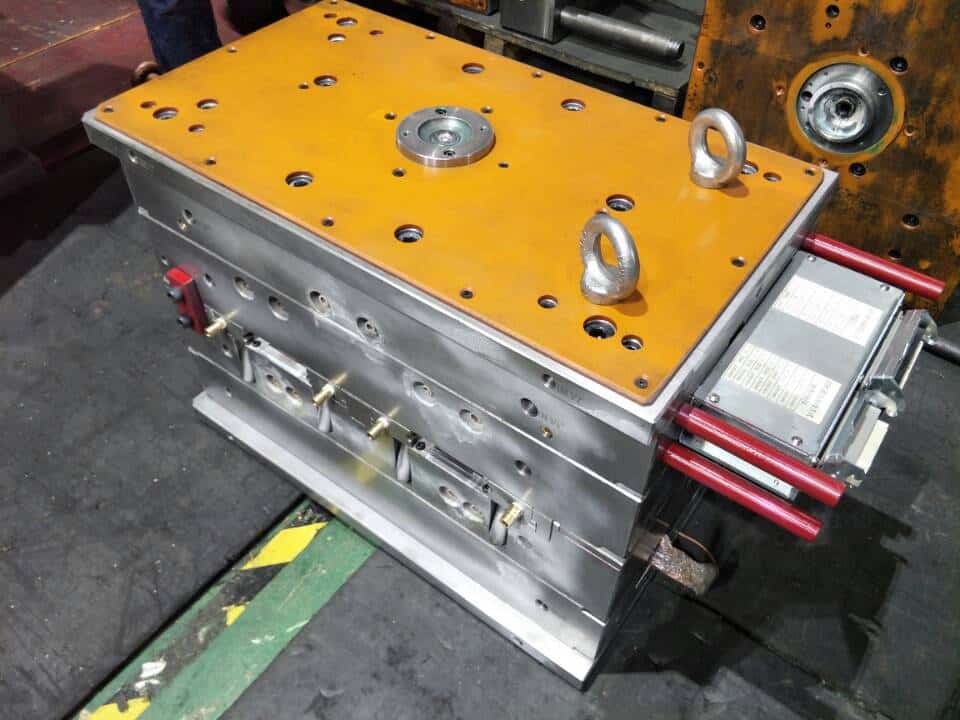

plastic injection mold
Reasons for gas generation during product manufacturing
1. The gas entrained by the material in the feeding system or the air in the cavity is not discharged from the runner and cavity in time during the forming process.
2. The resin is not sufficiently dry and contains water, which evaporates at the injection temperature and becomes steam.
3. The injection temperature is high, and the plastic decomposes to produce gas.
4. Some additives in the resin, volatilization or chemical reaction generate gas (for example, when thermosetting plastic is formed, not only does the plastic itself contain water and volatile components, but also condensation polymerization occurs during the curing process, producing condensed water and low molecular volatile gas).
5. Residual gas in resin.
Consequences of poor mold exhaust:
1. The gas undergoes large compression and generates back pressure, which increases the resistance of molten material to mold filling flow, prevents normal and rapid mold filling of molten plastic, prevents mold cavity from filling, and leads to unclear plastic edges.
2. There are obvious flow marks and fusion seams on the products, and the mechanical properties of the products decline.
3. After the gas is compressed, it will seep into the inner layer of the plastic, causing surface quality defects such as craze, air hole, loose tissue and peeling.
4. After the gas in the cavity is compressed, heat will be generated to raise the local temperature of the plastic, and the plastic melt will decompose and discolor, or even be charred and carbonized.
5. Poor exhaust reduces the filling speed, increases the forming cycle of parts (especially high-speed injection molding), and seriously affects the production efficiency.